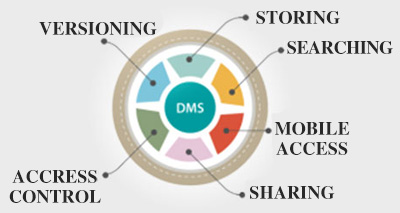
DMS Audit Trail
A document halts along several stops before it sees the light of day – and even after it does reach its intended final destination it has a defined life till which time it shall be retained. A document Audit Trail, as the name implies, is a formal, systematic and archived record or validation of the path followed by any document (and the ‘actions’ performed upon it) along its lifecycle journey. And it all begins with the ‘user’.
Users – ie, all workers of the organization or members of a particular project – are assigned rights to access and engage with the various documents in it. Depending on the sensitivity or significance of a particular document, different users can be assigned different levels of access rights, or denied the same via selective restrictions. In a large organisation this set-up may get unwieldy, so to better manage it access rights are delegated, with every team assigned a User Administrator to manage the access rights limited to their teams, making things more convenient and fast.
‘User Rights’ and ‘Delegation’ make ‘Audit Trails’ a necessary ‘Fall-back’ recourse to ensure the integrity and security of the organization’s critical documents.
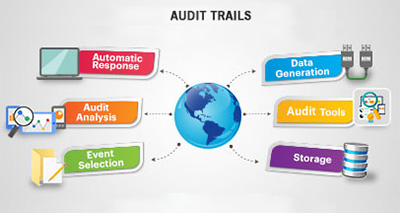
A typical DMS Audit Trail covers the following ‘actions’ that may have been performed upon the company’s documents by one or more ‘user’ – creation (of the document), viewing, modification, copying, deletion, searching, sharing, inviting other users, taking ownership of the content, starting a fresh ancillary theme or a new topic, and so on. A DMS Audit Trail sheds light on the ways in which people (who have shared access to a particular document) have interacted with it – and structurally comprises three elements: Login ID, a synopsis of system actions, and a time stamp.
For organisations that use a DMS fairly regularly (if not on a daily basis) to organise, share and store its files and documents, an Audit Trail becomes indispensable to the integrity of the system and the efficiency of its workflows.
For one thing, it allows you to keep a tab on the identity of team members who have been accessing the files and documents in the system.
Then, it can act as a ‘lifeline’ in cases where a change in the document needs to be un-done. Being a chronological record of document activities, all one has to do then, is refer to the version before the change.
A sophisticated (‘technologically advanced’) DMS usually also sports value-added features like built-in Trail or Audit functionality, notification or update functionality (when an unauthorized person uses or accesses a document), and Trail log protection (this ensures that a Document Audit Trail, once generated, cannot be deleted).